
About Laboratory Services
Clinica is allied with the foremost laboratory service provider in the country – Medlab Diagnostics Pvt Ltd. Which, therefore, ameliorates the quality of our services and accentuates our credibility.
General Blood Investigations
One of the most crucial ways to monitor your overall physical health is through routine blood testing. We can help you monitor how your body changes over time and provide you the information you need to make wise health decisions through these tests.
Some blood tests can help your doctor determine how different organs in your body are working. Examples of organs whose malfunctions can be visible in a blood test your thyroid, liver, or kidney.
Here are some of the routine test:
- Complete blood count
- Basic metabolic panel
- Comprehensive metabolic panel
- Lipid panel
- Thyroid panel
- Cardiac biomarkers
- Sexually transmitted infection tests
- Coagulation panel
Blood Typing

Your blood type is one of the things that can be measured with a blood test. Blood type is designated by two types of markers—the ABO type and the Rh type. A blood typing test detects the presence or absence of these markers.
The Plus sign indicated Rh markers, while the minus sign indicates Rh-negative.
Before transfusion, the recipient should be typed and their blood tested against the donor blood units (called a crossmatching test).
Urine Investigation
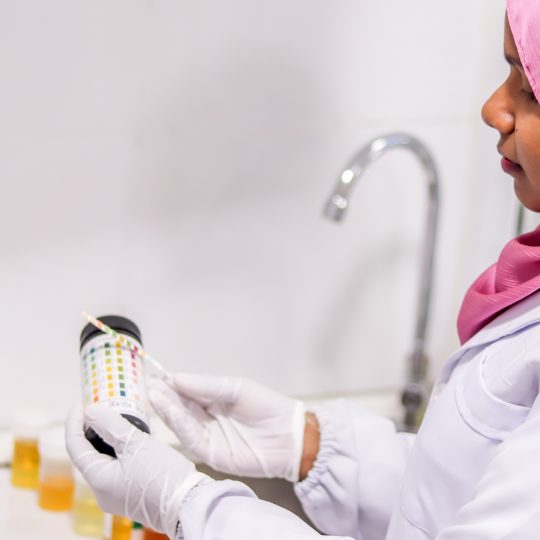

A urinalysis is a test of your
urine which is used to detect and manage a wide range of disorders, such as
urinary tract infections, kidney disease and diabetes.
A urinalysis involves checking
the appearance, concentration and content of urine. For instance, a urinary
tract infection can make urine look cloudy instead of clear. Increased levels
of protein in urine can be a sign of kidney disease.
A urinalysis might be part of a
routine medical exam, pregnancy checkup or pre-surgery preparation. A
urinalysis might be requested if you have abdominal pain, back pain, frequent
or painful urination, blood in your urine, or other urinary problems. If
you’ve been diagnosed with a medical condition, such as kidney disease or a urinary
tract infection, your doctor might recommend testing your urine regularly to
monitor your condition and treatment.
Other tests, such as pregnancy
testing and drug screenings, might rely on a urine sample.
Cultures
A bacteria culture test can help find harmful bacteria in or on your body that may be making you sick. Additionally, the test can identify what kind of bacteria caused the infection, which aids in making treatment choices. Our medical professionals will collect a sample of your blood, stool, urine, skin, mucus, or spinal fluid for a bacteria culture test. The type of sample depends on where the infection seems to be located.

Liver Studies
Liver function tests are blood tests used to help diagnose and monitor liver disease or damage. The tests measure the levels of certain enzymes and proteins in your blood.
Some of these tests measure how well the liver is performing its normal functions of producing protein and clearing bilirubin, a blood waste product. Other liver function tests measure enzymes that liver cells release in response to damage or disease. It can be used to Screen for liver infections, such as hepatitis, monitor the progression of a disease, such as viral or alcoholic hepatitis, and determine how well a treatment is working, measure the severity of a disease, particularly scarring of the liver (cirrhosis), monitor possible side effects of medications
Abnormal liver function test results don’t always indicate liver disease. Your doctor will explain your results and what they mean.
Thyroid Studies
The thyroid is a small gland located in the lower-front part of your neck. It’s responsible for helping regulate many bodily processes, such as metabolism, energy generation, and mood.
The thyroid produces two major hormones: triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). If your thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough of these hormones, you may experience symptoms such as weight gain, lack of energy, and depression. This condition is called hypothyroidism.
If your thyroid gland produces too many hormones, you may experience weight loss, high levels of anxiety, tremors, and a sense of being on a “high.” This is called hyperthyroidism.
Typically, a doctor who is concerned about your thyroid hormone levels will order broad screening tests, such as the T4 or the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) test. If those results come back abnormal, your doctor will order further tests to pinpoint the reason for the problem.
Lipid Studies
Lipid profile is a blood test that can measure the amount of cholesterol and triglycerides in your blood. This test can help determine your risk of the buildup of fatty deposits (plaques) in your arteries that can lead to narrowed or blocked arteries throughout your body (atherosclerosis). High cholesterol levels often are a significant risk factor for coronary artery disease. Prior testing patient must fast for 12 hours.
Diabetology
In order to treat diabetes in all its forms including diabetes mellitus, insulin-dependent diabetes (Type 1 diabetes), diabetes insipidus, and gestational diabetes. The test is commonly known as blood sugar levels. Blood sugar levels are tested in the laboratory based on two conditions i.e., fasting (FBS) or post prandial blood sugar (PPBS).
- For fasting blood sugar test patient has to be on fasting for 8 hour prior test.
- For post prandial blood sugar test patient has to come 2 hours after eating.
Electrolyte Studies
Electrolytes are substances that have a natural positive or negative electrical charge when dissolved in water. They help your body regulate chemical reactions, maintain the balance between fluids inside and outside your cells, and more. They’re also a key way to diagnose a wide range of medical conditions and diseases. Common electrolytes include, Sodium, potassium, calcium, chloride, magnesium, phosphorus.
Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases can be transferred from person to person by a variety of means – whether through airborne particles, bodily fluid exchange, or even a simple handshake – and can spread from host to host through both direct and indirect contact. Testing allows your doctor to verify if the symptoms you are experiencing are caused by an infectious disease.
These are illnesses that are brought on by pathogens (dangerous organisms) that enter your body from the outside. Flu, measles, HIV, strep throat, COVID-19 and salmonella are all examples.
Hygienic Screening
A basic hygienic screening would cover two main tests, Stool Full report and Stool Culture, which test for internal parasites. Food-borne illness like hepatitis A, Staph, E. coli and Salmonella are traced. We do hygienic screening test for hotel, restaurant, resort and food handling staffs.
Laboratory Services (Technical)
Hematology

Hematology is the branch of medicine that studies the causes, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases through the scientific examination of blood.
It entails treating diseases that affect blood production and its constituents, such as blood cells, hemoglobin, blood proteins, bone marrow, platelets, blood vessels, spleen, and the coagulation mechanism. Hemophilia, blood clots (thrombus), other bleeding disorders. These tests can also diagnose rare diseases such as blood cancers such as leukemia, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma are all examples of such diseases.
The laboratory analysis of blood is performed by a medical laboratory technologist.
Microbiology
Microbiology is the scientific study of microorganisms, which can be unicellular (single cell), multicellular (cell colony), or acellular (lacking cells). Virology, bacteriology, protistology, mycology, immunology, and parasitology are all sub-disciplines of microbiology.
Serology & Immunology
The scientific study of serum and other bodily fluids is known as serology.
In practice, the term usually refers to the identification of antibodies in serum for diagnostic purposes. Antibodies of this type are typically formed in response to an infection (against a specific microorganism), against other foreign proteins (for example, in response to a mismatched blood transfusion), or against one’s own proteins (in instances of autoimmune disease).
Immunology is a subfield of biology that studies immune systems in all organisms. Immunology charts, measures, and contextualizes the physiological functioning of the immune system in both healthy and disease states; immune system malfunctions in immunological disorders (such as autoimmune diseases, hypersensitivities, immune deficiency, and transplant rejection); and the physical, chemical, and physiological properties of immune system components in vitro, in situ, and in vivo. Immunology has applications in many areas of medicine, including organ transplantation, oncology, rheumatology, virology, bacteriology, parasitology, psychiatry, and dermatology.

Molecular Typing

Molecular typing is a manner of figuring out specific traces of microorganisms, which include microorganism or viruses, with the aid of using searching at their genetic material.
It is specifically used to pinpoint the supply of foodborne outbreaks. It also can be used to identify which microorganisms are most virulent and cause of critical diseases.
Histopathology
Histopathology refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist. Done in order to identify the disorders of tissues in your body.


